| | ||||||||||
| 1 | INN | Class | Route (list) | PK parameters= Cmax; Tmax; F: bioavailability; t1/2: half-life; VD: volume of distribution; Cl: clearance; PPB: plasma protein binding;(EQN means that the equation t1/2 = VD / Cl * 0.693 was used | Primary Target and PDB code of Protein-Drug complex | Targets from DrugCentral | Links | |||
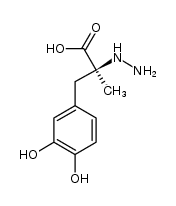
| CARBIDOPA (is an active metabolite)
| CARBIDOPA | NERVOUS SYSTEM | ORAL ENTERAL | Cmax 995 NANOMOLAR Tmax 2.95 HOUR F 99 PERCENT PPB 36 PERCENT HT 1.8 HOUR SOLUBILITY SLIGHTLY SOLUBLE IN WATER | AROMATIC-L-AMINO-ACID DECARBOXYLASE (AADC) PDB 1JS3 (CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF DOPA DECARBOXYLASE IN COMPLEX WITH THE INHIBITOR CARBIDOPA) LIGAND CODE = 142 (link to the list of PDB complexes) Download experimental 3D coordinates of 142 with added hydrogens | Aromatic-L-amino-acid decarboxylase UNIPROT P20711 DDC more at DrugCentral | EMA | |||
| 2 | INN | Class | Route (list) | PK parameters= Cmax; Tmax; F: bioavailability; t1/2: half-life; VD: volume of distribution; Cl: clearance; PPB: plasma protein binding;(EQN means that the equation t1/2 = VD / Cl * 0.693 was used | Primary Target and PDB code of Protein-Drug complex | Targets from DrugCentral | Links | |||
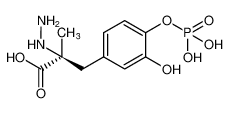
| FOSCARBIDOPA (has an active metabolite)
| FOSCARBIDOPA | NERVOUS SYSTEM | SUBCUTANEOUS | PPB 25 PERCENT SOLUBILITY FREELY SOLUBLE IN WATER | ALKALINE PHOSPHATASE | - more at DrugCentral | EMA | |||